Western Gull
The Washington representatives of this family can be split into two groups, or subfamilies. The adaptable gulls are the most familiar. Sociable in all seasons, they are mainly coastal, but a number of species also nest inland. Many—but not all—are found around people. Gulls have highly variable foraging techniques and diets. Terns forage in flight, swooping to catch fish or insects. They dive headfirst into the water for fish. Although they are likely to be near water, they spend less time swimming than gulls.
General Description
The adult Western Gull has a deep gray back and wings, with black wing-tips that blend into the rest of the wing, unlike many species where the black is clearly defined. The underwing is white with a narrow band of gray. The head is mostly white, with a limited amount of brown streaking, especially in non-breeding plumage. The large bill is yellow with a red spot, and the eye is dark yellow. Like the other large gulls in Washington, the Western Gull is a four-4 year gull, meaning that it takes four years to achieve adult plumage. Juveniles are mottled brown, with a dark bill and dark eyes, and pinkish-gray legs. This plumage varies and takes on more of the adult plumage characteristics in each successive year. At the northern extent of their breeding range in Washington, Western Gulls frequently hybridize with Glaucous-winged Gulls and often display intermediate plumage characteristics, leading to identification confusion between these and other large gulls found here. An advanced field guide and assistance from an experienced observer are highly beneficial for descriptions of hybrids and identification of gulls.
Habitat
Western Gulls are found mostly near the coast, and also found regularly offshore. They are not typically found far inland. Many types of habitats are used, including estuaries, beaches, fields, garbage dumps, and city waterfronts. Nest sites are often located on rocky, sandy, or gravel islands, or inaccessible mainland cliffs.
Behavior
Opportunistic, the Western Gull will steal unguarded eggs or chicks of other species, near which they often locate their nesting colonies. They will also situate colonies near sea lion breeding colonies and scavenge dead pups. Western Gulls, like many other gull species, drop hard-shelled items from the air to break them on hard surfaces. In very hot weather, adults may cool their eggs with their wet belly feathers.
Diet
Western Gulls are omnivores and eat a variety of things including fish and other aquatic creatures, eggs, carrion, garbage, and other birds.
Nesting
Western Gulls nest in colonies on islands, offshore rocks, and abandoned piers. Colonies are often located near nesting seabirds or sea lions. Birds first breed at the age of 4 years. Nests are built on the ground, and the pair often starts as many as three nests, and then chooses one to finish and use. The nest is often located next to a rock or other object that provides protection from the wind and a visual barrier from neighbors. The nest is a substantial mound built from nearby vegetation and debris. The female usually lays 3 eggs. (Nests with more than three eggs are the result of multiple females.) Both members of the pair incubate the eggs for about a month. A few days after hatching, the young may leave the nest but won't go far, often hiding in nearby vegetation. At 6 to 7 weeks of age, they begin to fly, but don't become independent from their parents and depart the colony until they are 10 weeks or older.
Migration Status
Western Gulls are present year round throughout the breeding range, although birds wander widely within this range.
Conservation Status
The Western Gull is limited in distribution with a smaller population size than most other North American gulls, with a total population of only 40,000 pairs worldwide, limited to about 200 colonies. The number of Western Gulls in Washington is difficult to determine because of their extensive hybridization with Glaucous-winged Gulls in this state. Some say that the population is stable or increasing. Others claim that the Western Gull is one of the most limited North American Gulls in range and population numbers, and may become a species of concern if the current practice of management decisions favoring other species over Western Gulls continues.
When and Where to Find in Washington
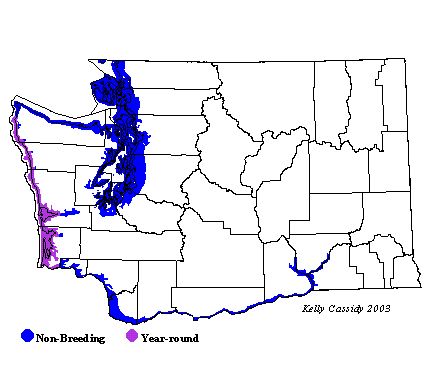
Western Gulls are common in all seasons along the Washington coast. The northern edge of the breeding range of pure Western Gulls is at Tatoosh Island in Washington, and south of Grays Harbor, most of the gulls are pure Western Gulls. Many of the birds breeding in Grays Harbor are hybrids. The hybrid zone extends farther to the north, but not into British Columbia. Large colonies of Western Gulls can be found at Grays Harbor, Willapa Bay, and the mouth of the Columbia River. Western Gulls have been recorded east of the Cascades, but are predominantly seen on the coast.
 Abundance
Abundance
| Ecoregion | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oceanic | C | C | C | C | C | C | C | C | C | C | C | C |
| Pacific Northwest Coast | C | C | C | C | C | C | C | C | C | C | C | C |
| Puget Trough | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | U |
| North Cascades | ||||||||||||
| West Cascades | R | R | R | R | ||||||||
| East Cascades | ||||||||||||
| Okanogan | ||||||||||||
| Canadian Rockies | ||||||||||||
| Blue Mountains | ||||||||||||
| Columbia Plateau |
Washington Range Map
North American Range Map

Family Members
 Laughing GullLarus atricilla
Laughing GullLarus atricilla Franklin's GullLarus pipixcan
Franklin's GullLarus pipixcan Little GullLarus minutus
Little GullLarus minutus Black-headed GullLarus ridibundus
Black-headed GullLarus ridibundus Bonaparte's GullLarus philadelphia
Bonaparte's GullLarus philadelphia Heermann's GullLarus heermanni
Heermann's GullLarus heermanni Black-tailed GullLarus crassirostris
Black-tailed GullLarus crassirostris Short-billed GullLarus canus
Short-billed GullLarus canus Ring-billed GullLarus delawarensis
Ring-billed GullLarus delawarensis California GullLarus californicus
California GullLarus californicus Herring GullLarus argentatus
Herring GullLarus argentatus Thayer's GullLarus thayeri
Thayer's GullLarus thayeri Iceland GullLarus glaucoides
Iceland GullLarus glaucoides Lesser Black-backed GullLarus fuscus
Lesser Black-backed GullLarus fuscus Slaty-backed GullLarus schistisagus
Slaty-backed GullLarus schistisagus Western GullLarus occidentalis
Western GullLarus occidentalis Glaucous-winged GullLarus glaucescens
Glaucous-winged GullLarus glaucescens Glaucous GullLarus hyperboreus
Glaucous GullLarus hyperboreus Great Black-backed GullLarus marinus
Great Black-backed GullLarus marinus Sabine's GullXema sabini
Sabine's GullXema sabini Black-legged KittiwakeRissa tridactyla
Black-legged KittiwakeRissa tridactyla Red-legged KittiwakeRissa brevirostris
Red-legged KittiwakeRissa brevirostris Ross's GullRhodostethia rosea
Ross's GullRhodostethia rosea Ivory GullPagophila eburnea
Ivory GullPagophila eburnea Least TernSternula antillarum
Least TernSternula antillarum Caspian TernHydroprogne caspia
Caspian TernHydroprogne caspia Black TernChlidonias niger
Black TernChlidonias niger Common TernSterna hirundo
Common TernSterna hirundo Arctic TernSterna paradisaea
Arctic TernSterna paradisaea Forster's TernSterna forsteri
Forster's TernSterna forsteri Elegant TernThalasseus elegans
Elegant TernThalasseus elegans

